Fungal nail infection (also known as onychomycosis) refers to an infection of the toe- or fingernails by fungi (dermatophytes). The prevalence is estimated between 20-25 % of the population. It is important to treat fungal nail infection as soon as possible because the infection is contagious. In most cases fungal nail infections tend to look unhygienic. The infection usually starts at the rim of the nail, which changes colour to whitish-yellow, brown or green. The fungus grows under or into the nail causing the nail plate to thicken and crumble. Sometimes the nail becomes partially or completely detached, which may be painful. In some cases the nail will completely release from the toe or finger.
Nails are infected by fungus due to nail (sports) trauma, excessive moisture, heat, perspiration or poor foot hygiene. Fungi are therefore typically found in bathrooms, dressing rooms and showers within sports clubs, around swimming pools and saunas. In instances of athletes foot (this is a different kind of fungus that can be found on top of the skin between the toes) there is a chance of contamination and this fungus can also lead to fungal nail infections.
How do you know you have a fungal nail infection? It's not always easy to confirm, but there are a number of common symptoms that point in that direction:
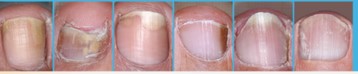
Fungal nail infection (onychomycosis) is a progressive disease. If it is left untreated the infection spreads. Initially you may only see white spots or patches on the nail. They only affect the cosmetic appearance of the nail and initially there is no pain. If your nail is showing symptoms, it is important to take immediate action as the fungus will gradually spread throughout the nail. If left untreated, you will run the risk of the nail becoming brittle and a possibility that you may lose the nail. The infection can spread between fingernails and toenails and from one person to another.